Imagine a natural compound that has been used for centuries in ancient healing practices yet still holds incredible promise in today's modern world. Meet berberine, a fascinating substance derived from plants and valued in traditional Chinese medicine and Ayurvedic medicine for its remarkable therapeutic properties. But here's the exciting part: Berberine isn't just some forgotten remedy of the past; it has captured the attention of researchers worldwide due to its impressive pharmacological effects. From fighting microbes to combating inflammation and even helping to regulate blood glucose levels, berberine has diverse potential benefits. It might be the solution to treating some conditions without the need for antibiotics. If you're interested in learning more about this incredible natural chemical and how it may transform your attitude towards health, get ready because we're about to go on an adventure into the enthralling world of berberine.
Author
Dr. Ayesha Tufail
Certified Medical Doctor, Researcher and Top-Rated Medical Writer on Upwork. Dr. Ayesha Tufail has more than 10 years of experience working as a General Practitioner. Her areas of research include Stem Cell Therapy, Herbal Health Supplements & Adult ADHD.
You can get in touch with Dr. Ayesha via her LinkedIn account linked at the end of this page.
What is Berberine?
Berberine, also known as berberine HCl, is a naturally occurring compound classified as an isoquinoline alkaloid. Derived from plants like barberry and goldenseal, berberine has been used in traditional medicine systems for centuries. Berberine exhibits a wide range of pharmacological activities, making it a subject of significant scientific interest. It has been associated with potential benefits such as antihypertensive, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antidepressant, anticancer, anti-diarrheal, and hepatoprotective effects. Overall, berberine is a bioactive compound that has generated considerable interest for its diverse therapeutic properties, making it a subject of ongoing research and exploration in the field of medicine.
Health Benefits of Berberine:
Berberine has been studied extensively for its potential health benefits. Some of the potential health benefits associated with berberine include:
Berberine has demonstrated promising effects in controlling blood sugar levels, particularly in individuals with type 2 diabetes. This natural compound has been found to enhance insulin sensitivity and reduce insulin resistance, leading to improved glucose metabolism. By targeting key molecular pathways involved in blood sugar regulation, berberine can help lower fasting blood glucose levels and glycated haemoglobin (HbA1c), a measure of long-term blood sugar control.
Studies have shown that berberine's ability to activate AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and improve glucose uptake in cells plays a significant role in its antidiabetic effects. Furthermore, berberine may also inhibit enzymes responsible for carbohydrate metabolism in the gut, thereby reducing the absorption of glucose from the diet. These findings suggest that berberine has the potential to be a valuable adjunctive therapy for individuals with type 2 diabetes, aiding in the management of their blood sugar levels and improving overall glycemic control.
Berberine has shown the potential in improving both high blood pressure and cholesterol levels, making it beneficial for cardiovascular health. Studies have indicated that berberine can help lower blood pressure by relaxing blood vessels and reducing peripheral resistance. This effect may be attributed to its ability to enhance nitric oxide production, which promotes vasodilation and improves blood flow. By reducing blood pressure, berberine may help reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases such as heart attacks and strokes.
Additionally, berberine has been found to have positive effects on lipid profiles. It can lower total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol (often referred to as "bad" cholesterol), and triglyceride levels. At the same time, it can increase HDL cholesterol (referred to as "good" cholesterol). By improving the balance of these lipid parameters, berberine may help reduce the risk of atherosclerosis and other cardiovascular complications.
The mechanisms by which berberine exerts its effects on blood pressure and cholesterol levels are still being studied. However, it is believed to involve multiple pathways, including modulation of lipid metabolism, inhibition of cholesterol synthesis, and regulation of genes involved in lipid regulation.
Berberine's positive effects on heart health can be attributed to its ability to regulate blood sugar levels and combat obesity, both of which are risk factors for coronary heart disease. Additionally, berberine promotes the release of nitric oxide, a molecule that relaxes the arteries, improves blood flow, lowers blood pressure, and helps protect against arteriosclerosis.
Research published in the World Journal of Cardiology revealed that individuals taking berberine experienced improved heart function and exercise capacity compared to those taking a placebo. Furthermore, berberine shows potential in the treatment of arrhythmias and heart failure. These cardiovascular benefits highlight berberine's potential in supporting overall heart health.
Berberine has shown potential in protecting against cognitive decline and offering benefits for brain health. Studies suggest that berberine possesses neuroprotective properties, including antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. These properties help combat oxidative stress and reduce inflammation, which is associated with neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's. Additionally, berberine may enhance brain function by promoting the clearance of abnormal protein deposits in the brain, a hallmark of neurodegenerative conditions. While more study is needed to completely understand berberine's processes in cognitive decline, its potential as a neuroprotective agent makes it a potential option for sustaining brain health and perhaps lowering the risk of mental problems.
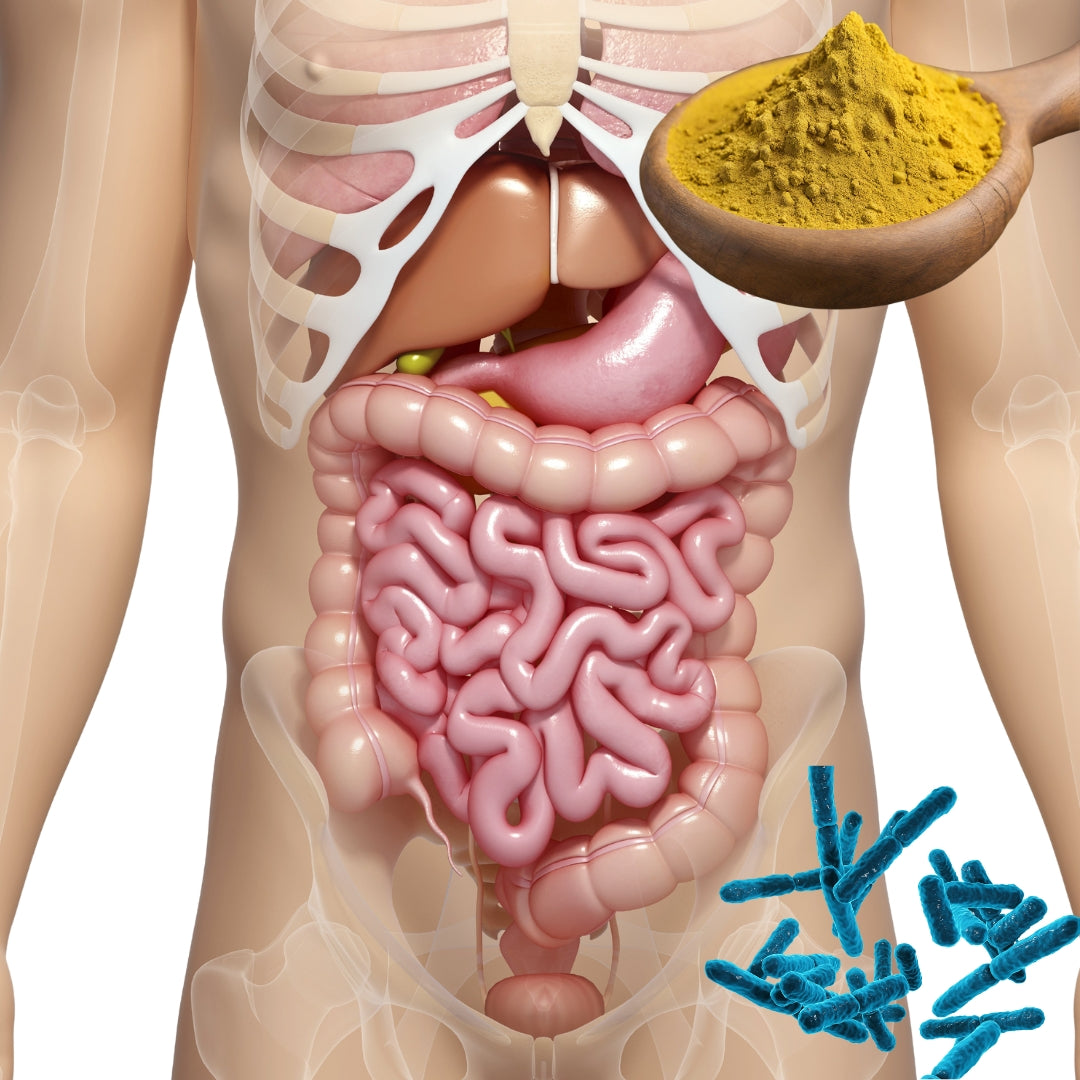
Berberine plays a significant role in promoting gastrointestinal health and addressing various gastrointestinal conditions. Its beneficial effects are attributed to its antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, and anti-diarrheal properties.
Berberine has been shown to have antimicrobial activity against a wide range of pathogens, including bacteria, fungi, viruses, and parasites. This makes it effective in fighting gastrointestinal infections and reducing the growth of harmful microorganisms in the gut.
Furthermore, berberine exhibits anti-inflammatory properties that can help alleviate inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract. It may reduce gut inflammation associated with conditions like inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), providing relief from symptoms such as abdominal pain and diarrhoea.
Berberine's anti-diarrhoeal effects make it useful in managing diarrhoea, particularly acute infectious diarrhoea and traveller's diarrhoea. It can help regulate bowel movements and reduce the frequency and severity of loose stools.
Moreover, berberine has shown potential in promoting a healthy gut microbiota balance. It can modulate the composition of gut bacteria, increasing the abundance of beneficial bacteria and inhibiting the growth of harmful bacteria. Maintaining a healthy balance of gut microbiota is essential for proper digestion and overall gastrointestinal health.
Berberine has emerged as a potential aid in weight management due to its effects on various aspects of metabolism and body composition. Research suggests that berberine can help regulate weight by influencing multiple pathways involved in energy balance.
One key mechanism is its ability to activate an enzyme called AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), which helps regulate metabolism and energy expenditure. By activating AMPK, berberine can enhance fat oxidation, increase glucose uptake, and promote the breakdown of fatty acids, ultimately leading to a reduction in body weight.
Berberine has also been found to inhibit the production and accumulation of fat cells by suppressing the activity of certain enzymes involved in lipogenesis, the process of fat formation. This can help prevent the excessive storage of fat and contribute to weight loss. Furthermore, berberine has shown potential in improving insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism. By enhancing insulin action, berberine can help regulate blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of insulin resistance, which is often associated with weight gain and obesity.
Additionally, berberine may impact appetite control by modulating certain hormones involved in hunger and satiety. Studies have suggested that berberine can decrease levels of the hunger hormone ghrelin and increase levels of the satiety hormone leptin, which may lead to reduced food intake and a more incredible feeling of fullness. While berberine shows promise in weight management, it is important to note that it should be used in conjunction with a balanced diet, regular exercise, and lifestyle modifications.
Research suggests that berberine possesses anticancer potential, exhibiting inhibitory effects on various stages of cancer development and progression. Studies have shown that berberine can suppress the growth and proliferation of cancer cells by inducing cell cycle arrest and promoting apoptosis (programmed cell death) in different types of cancer, including breast, lung, liver, prostate, and colon cancer.
Berberine has also demonstrated the ability to inhibit tumour angiogenesis, the process by which tumours develop new blood vessels to support their growth. By blocking angiogenesis, berberine can restrict the blood supply to tumours, impeding their ability to thrive and metastasise.
Furthermore, berberine has been shown to exert anti-metastatic effects by inhibiting the invasion and migration of cancer cells. It can modulate the expression of genes and proteins involved in these processes, thereby reducing the likelihood of cancer spreading to other organs.
In addition to its direct effects on cancer cells, berberine has shown potential in enhancing the efficacy of chemotherapy and radiotherapy. It can sensitise cancer cells to these treatments, making them more susceptible to their effects.
However, it's important to note that while berberine holds promise in cancer treatment, further research is needed to fully understand its mechanisms and potential clinical applications.
According to research, berberine may have a beneficial role in the management of polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS). It has shown potential in improving insulin sensitivity, regulating menstrual cycles, reducing testosterone levels, and supporting weight management in women with PCOS. By addressing these key aspects, berberine may help restore hormonal balance, promote ovulation, and improve metabolic health in PCOS patients. However, further research is needed to fully understand its mechanisms and establish its long-term safety and efficacy.
Berberine possesses significant antimicrobial properties, making it effective against a wide range of microorganisms, including bacteria, fungi, viruses, and parasites. Its ability to inhibit the growth and survival of these pathogens has been extensively studied.
In bacterial infections, berberine has shown efficacy against various strains, including those resistant to conventional antibiotics. It can disrupt bacterial cell membranes, interfere with essential cellular processes, and inhibit bacterial adhesion and biofilm formation. This makes it a potential alternative or adjunct therapy for bacterial infections.
Berberine also exhibits antifungal activity against different types of fungi, including Candida species, which are responsible for various infections. It can disrupt fungal cell membranes, inhibit fungal growth, and reduce the formation of fungal biofilms.
Additionally, berberine has demonstrated antiviral properties against several viruses, including the hepatitis B virus (HBV), influenza virus, herpes simplex virus (HSV), and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). It can inhibit viral replication, reduce viral load, and interfere with viral entry into host cells.
Berberine has also been used to treat parasitic diseases like malaria and leishmaniasis. It can inhibit the growth of parasites, disrupt their cellular functions, and impair their survival. The antimicrobial properties of berberine are attributed to its ability to interact with microbial DNA, enzymes, and cellular structures.
Berberine Supplements:
Berberine supplements can be derived from various natural sources, each with its own unique characteristics. Here are some different types of berberine supplements based on their sources:
1. Berberine from Berberis Species:
Berberis plants, such as Berberis aristata (Indian barberry) or Berberis vulgaris (European barberry), are a common source of berberine. Extracts from the roots, stems, and bark of these plants are used to produce berberine supplements. Berberis-derived berberine has been traditionally used in Ayurvedic and Chinese medicine for its medicinal properties.
2. Berberine from Coptis Species:
Coptis chinensis (Chinese goldthread) is a medicinal herb that contains high levels of berberine. Berberine, derived from Coptis chinensis, is often used in traditional Chinese medicine formulations. It is considered potent and highly regarded for its therapeutic properties.
3. Berberine from Phellodendron Species:
Phellodendron amurense (Amur cork tree) is another source of berberine. Extracts from the bark of this tree contain berberine and are utilized in the production of berberine supplements. Phellodendron-derived berberine is known for its potential health benefits and has been studied for its various pharmacological activities.
4. Synthetic Berberine:
In addition to natural sources, berberine can also be synthesised in a laboratory setting. Synthetic berberine is chemically identical to naturally-derived berberine. It may be used in certain berberine supplements, offering a reliable and consistent source of the compound.
When selecting a berberine supplement, it is important to consider the source and quality of the berberine used. The effectiveness and bioavailability of berberine can vary depending on the extraction process and the purity of the compound.
Recommended Dosage of Berberine:
The recommended dosage of berberine can vary depending on the specific health condition being targeted and the formulation of the supplement. However, a commonly suggested dosage range for berberine is 500 to 1500 milligrams per day, divided into two to three doses. It is advisable to start with a lower dosage and gradually increase it while monitoring its effects. Berberine should be taken with meals to enhance absorption and minimise the risk of gastrointestinal side effects.
Potential Side Effects and Drug Interactions:
Berberine is generally considered safe for most individuals, but it can potentially cause side effects and interact with certain medications. Common side effects of berberine include gastrointestinal issues such as diarrhoea, constipation, abdominal discomfort, and bloating.
Berberine has the potential to interact with medications metabolised by the liver enzymes CYP3A4 and CYP2D6. This can affect the effectiveness or increase the side effects of certain medications, including statins, blood pressure medications, immunosuppressants, and anticoagulants. Additionally, berberine may lower blood sugar levels, so caution is advised for individuals with diabetes or those taking medications to control blood sugar. Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels and potential dosage adjustments under medical supervision may be necessary.
Additionally, it is advised against taking berberine supplements while expecting or nursing unless specifically instructed to do so by a medical professional. In rare cases, some individuals may experience allergic reactions to berberine. If you develop symptoms such as rash, itching, swelling, or difficulty breathing, discontinue use and seek medical attention promptly.
Final Thoughts:
In conclusion, berberine supplements offer a wide range of potential health benefits, including blood sugar control, cardiovascular support, weight management, and gastrointestinal health improvement. With its versatile properties and positive research findings, berberine HCl is an enticing supplement to consider for overall well-being.
If you're ready to experience the potential benefits of berberine, take the next step and consider purchasing a high-quality berberine HCl supplement. However, it's essential to consult with a healthcare professional before incorporating any new supplement into your routine, especially if you have specific health concerns or are taking medications. Explore the advantages of berberine HCl supplements right now to make a smart decision, put your health first, and start down the path to greater well-being.
Medical Disclaimer: While we have delve into the research available on the health benefits of these awesome supplements we offer, this is for informative purposes only and shouldn’t be taken as medical advice. Those who have any health-related queries should reach out to a medical professional. These statements have not been evaluated by the Therapeutic Goods Administration. This article is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.
Dr. Ayesha Tufail's LinkedIn - www.linkedin.com/in/dr-ayesha-tufail-679176252/
References:
- Amritpal, S., Sanjiv, D., Navpreet, K., & Jaswinder, S. (2010). Berberine: alkaloid with wide spectrum of pharmacological activities. Journal of Natural Products (India), 3, 64-75.
-
Affuso, F., Mercurio, V., Fazio, V., & Fazio, S. (2010). Cardiovascular and metabolic effects of Berberine. World Journal of Cardiology, 2(4), 71-77. https://doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v2.i4.71
-
Zhu, L., Gu, P., & Shen, H. (2019). Protective effects of berberine hydrochloride on DSS-induced ulcerative colitis in rats. International Immunopharmacology, 68, 242-251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2018.12.036
-
Xu, J., Long, Y., Ni, L. et al. Anticancer effect of berberine based on experimental animal models of various cancers: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Cancer 19, 589 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-019-5791-1
- Guo J, Chen H, Zhang X, Lou W, Zhang P, Qiu Y, Zhang C, Wang Y, Liu WJ. The Effect of Berberine on Metabolic Profiles in Type 2 Diabetic Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021 Dec 15;2021:2074610. doi: 10.1155/2021/2074610. PMID: 34956436; PMCID: PMC8696197.
-
Grassi, D., Necozione, S., Desideri, G., Abballe, S., Mai, F., Feo, M. D., Carducci, A., & Ferri, C. (2021). Acute and Long Term Effects of a Nutraceutical Combination on Lipid Profile, Glucose Metabolism and Vascular Function in Patients with Dyslipidaemia with and Without Cigarette Smoking. High Blood Pressure & Cardiovascular Prevention, 28(5), 483-491. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40292-021-00468-4
-
Elisa Pierpaoli, Oscar Cirioni, Oriana Simonetti, Fiorenza Orlando, Andrea Giacometti, Paolo Lombardi & Mauro Provinciali (2021) Potential application of berberine in the treatment of Escherichia coli sepsis, Natural Product Research, 35:22, 4779-4784, DOI: 10.1080/14786419.2020.1721729
-
Neag, M. A., Mocan, A., Echeverría, J., Pop, R. M., Bocsan, C. I., Crişan, G., & Buzoianu, A. D. (2018). Berberine: Botanical Occurrence, Traditional Uses, Extraction Methods, and Relevance in Cardiovascular, Metabolic, Hepatic, and Renal Disorders. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 9. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2018.00557
- Mishra, N., Verma, R., & Jadaun, P. (2022). Study on the Effect of Berberine, Myoinositol, and Metformin in Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: A Prospective Randomised Study. Cureus, 14(1). https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.21781