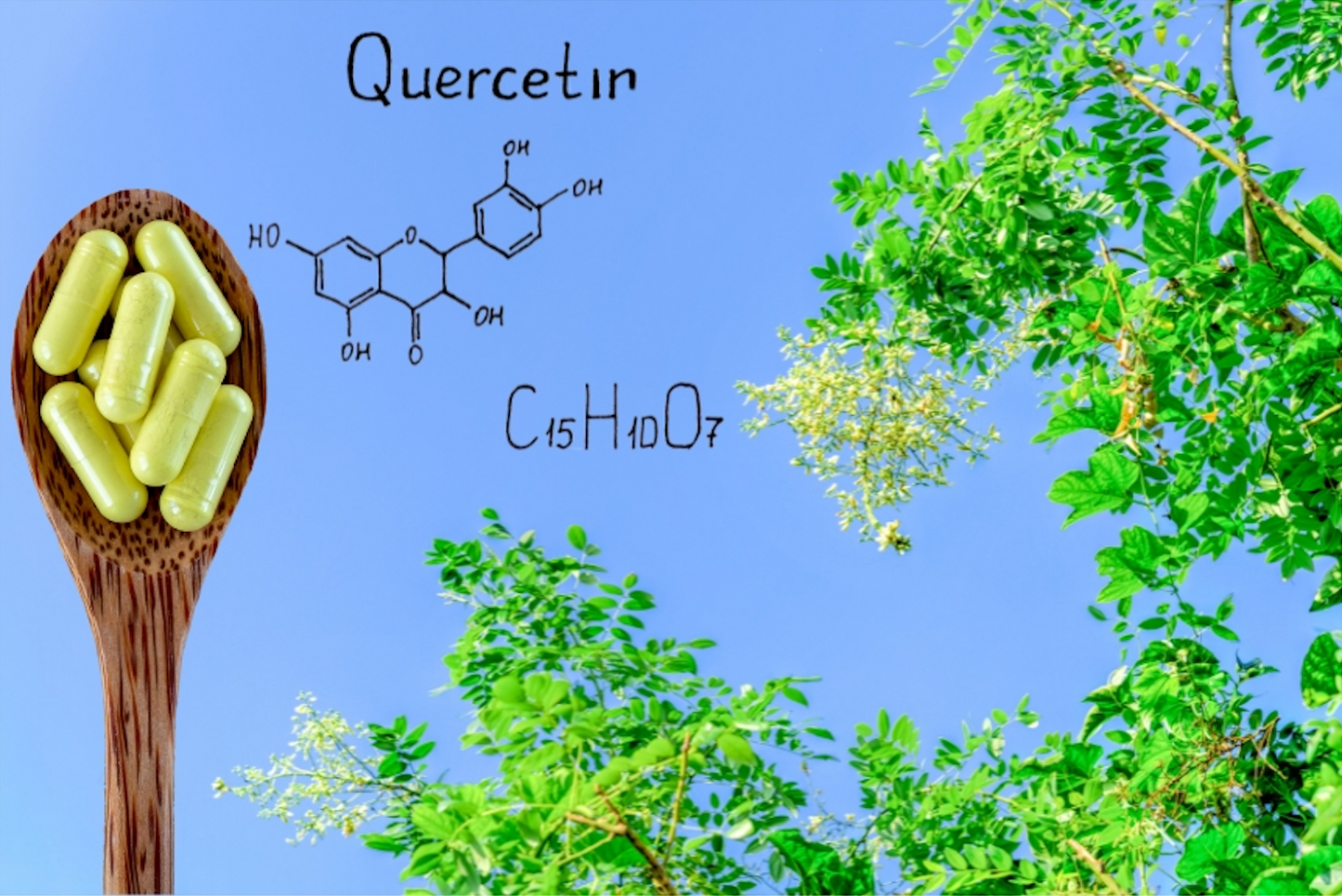
Are you searching for a natural remedy to combat allergies and support your overall well-being? Look no further than quercetin, a versatile compound found in various fruits, vegetables, and grains. But did you know that quercetin's benefits extend beyond just allergy relief? How does this great flavonoid help alleviate allergic reactions, and what other wonders does it hold? Join us to explore quercetin's antiallergic potential while discovering its antioxidant powers, anti-inflammatory effects, and promising impact on heart health and immune function. Discover the secrets of this extraordinary compound that nature has bestowed upon us.
Author
Dr. Ayesha Tufail
Certified Medical Doctor, Researcher and Top-Rated Medical Writer on Upwork. Dr. Ayesha Tufail has more than 10 years of experience working as a General Practitioner. Her areas of research include Stem Cell Therapy, Herbal Health Supplements & Adult ADHD.
You can get in touch with Dr. Ayesha via her LinkedIn account linked at the end of this page.
What is Quercetin?
Quercetin is a natural plant pigment known as a flavonoid, commonly found in fruits, vegetables, and grains. It is renowned for its antioxidant properties, which help prevent harmful free radicals from damaging the body's cells. Quercetin also exhibits anti-inflammatory effects, making it potentially beneficial for conditions like arthritis and allergies. This compound has various health benefits, including supporting heart health, immune system function, and allergy relief by reducing histamine release. Quercetin is available in supplement form, offering a convenient way to incorporate this powerful flavonoid into your daily routine for optimal health and well-being.
Natural Sources of Quercetin:
Quercetin is naturally found in a variety of fruits, vegetables, and other plant-based foods. Here are some common natural sources of quercetin:
1. Fruits:
Apples, grapes, cherries, citrus fruits (such as oranges and grapefruits), berries (such as blueberries and cranberries), and tropical fruits (such as mangoes and papayas) are known to contain quercetin.
2. Vegetables:
Onions, shallots, garlic, capers, broccoli, kale, spinach, tomatoes, red leaf lettuce, and red bell peppers are among the vegetables that contain quercetin.
3. Herbs and Spices:
Dill, cilantro, parsley, lovage, sage, thyme, and chilli peppers are herbs and spices that can provide quercetin.
4. Legumes:
Quercetin is found in foods like lentils, black beans, and kidney beans.
5. Nuts and Seeds:
Almonds, pistachios, and buckwheat are examples of nuts and seeds that contain quercetin.
6. Beverages:
Green tea and black tea are known to have quercetin, with green tea generally containing higher amounts.
Health Benefits of Quercetin:
Quercetin, a natural flavonoid, offers a range of health benefits supported by scientific research. Here are some of the key health benefits associated with quercetin:
Quercetin exhibits potent anti-inflammatory effects by inhibiting inflammatory enzymes like COX-2 and LOX, reducing the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, interfering with inflammatory signalling pathways such as NF-kB, and acting as an antioxidant to reduce oxidative stress. These properties help quercetin suppress inflammation and alleviate its associated symptoms. By modulating immune responses and promoting a balanced inflammatory environment, quercetin shows potential for managing chronic inflammatory conditions like arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease. While more research is needed, quercetin's anti-inflammatory effects make it a promising natural compound for supporting overall health and combating inflammation-related diseases.
Quercetin exhibits potent antioxidant effects due to its ability to scavenge free radicals and protect against oxidative stress. As a potent antioxidant, quercetin helps neutralise harmful reactive oxygen species and prevent cellular damage. It also enhances the activity of endogenous antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase and glutathione peroxidase. By reducing oxidative stress, quercetin contributes to the prevention of chronic diseases, supports cardiovascular health, and may play a role in neuroprotection. The antioxidant properties of quercetin highlight its potential as a natural defence against oxidative damage and its significance in promoting overall well-being.
Quercetin exhibits notable anti-allergic effects, making it a promising compound for allergy relief. It acts by inhibiting the release of histamine, a key player in allergic reactions. By stabilising mast cells and basophils, quercetin helps prevent histamine release and reduce allergic symptoms such as sneezing, itching, and nasal congestion. Additionally, quercetin's anti-inflammatory properties help alleviate inflammation associated with allergies. Studies have shown that quercetin supplementation may provide relief for various allergic conditions, including hay fever and allergic asthma. Due to its anti-allergic properties, quercetin is recognised as a safe and effective natural remedy for treating and reducing allergy-related discomfort.
Quercetin offers potential antimicrobial benefits and immune system support. Its antimicrobial properties have been observed against various microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites. Quercetin can inhibit their growth and replication, potentially aiding in the prevention and treatment of infections. Additionally, quercetin has immune-modulating effects, enhancing the activity of immune cells like natural killer (NK) cells and T lymphocytes. It also regulates cytokine production, which is crucial for immune response coordination. Quercetin's anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties further contribute to its immune-boosting potential. While further research is required, quercetin shows promise as a natural compound for supporting immune health and combating microbial threats
Quercetin has been studied for its potential to support heart health and promote cardiovascular well-being. It exhibits several properties that contribute to its beneficial effects on the cardiovascular system. Quercetin helps reduce oxidative stress and inflammation, which are key factors in the development of heart disease. It can improve blood vessel function by promoting vasodilation and reducing blood pressure. Additionally, quercetin has been shown to inhibit the oxidation of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, thus reducing the risk of plaque formation and atherosclerosis. These combined effects suggest that quercetin may help maintain healthy heart function and reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases when incorporated into a balanced lifestyle.
Quercetin has shown promising potential for protecting liver health. Research studies have revealed its hepatoprotective effects in various scenarios. In cases of ethanol-induced acute liver injury, quercetin has been found to increase the activity of ethanol-metabolizing enzymes, enhance antioxidant defences against oxidative stress, and reduce the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines. Additionally, quercetin has been shown to attenuate liver inflammation and fibrosis by inhibiting macrophage infiltration. These findings suggest that quercetin may play a role in preventing liver damage, promoting liver cell health, and potentially serving as a therapeutic agent for liver diseases. Further research is needed to fully understand the mechanisms and potential applications of quercetin in liver health.
Studies suggest that quercetin may have neuroprotective effects by reducing oxidative stress and inflammation in the brain, which are associated with age-related cognitive decline and neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's. Quercetin's ability to cross the blood-brain barrier allows it to exert its beneficial effects directly in the brain. Additionally, quercetin has been shown to enhance cognitive function, memory, and learning in animal studies. While more research is needed to fully understand the mechanisms, quercetin shows promise for supporting brain health and preserving cognitive function.
Quercetin, a potent flavonoid, offers skin health benefits by blocking mast cells involved in triggering allergic and inflammatory reactions. It protects against skin disorders like dermatitis and photosensitivity by exhibiting antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. Quercetin blocks the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines, providing relief from skin inflammation even for those unresponsive to conventional treatments. As an oral supplement, quercetin helps fight allergic and inflammatory diseases by inhibiting histamine secretion and reducing pro-inflammatory markers. Its ability to alleviate the symptoms of conditions like eczema makes quercetin a valuable option for promoting skin health and managing skin-related concerns.
Quercetin, a powerful antioxidant found in plant foods, has demonstrated potential as an anticancer agent. It exerts preventive and therapeutic effects against various types of cancer due to its broad range of activity, low toxicity, and natural origin. Quercetin has been explored as an alternative treatment, either alone or in combination with chemotherapy drugs. Its mechanisms of action include combating free radicals, reducing inflammation, and inhibiting cancer cell growth. Although more research is needed, quercetin shows promise as a complementary medicine for cancer prevention and treatment, offering a safe and cost-effective approach to fighting against this devastating disease.
Quercetin, a natural flavonoid, has been studied for its potential to enhance energy levels and improve endurance. It supports mitochondrial function, the powerhouse of cells responsible for energy production. By optimising mitochondrial performance, quercetin may enhance energy production and utilisation. It also increases oxygen uptake and utilisation during physical activity, improving endurance by delivering more oxygen to the muscles. Quercetin's anti-fatigue effects combat oxidative stress and inflammation, reducing exercise-induced fatigue. Additionally, its ability to improve blood flow and nutrient delivery to muscles supports energy production and endurance. While further research is needed, quercetin shows promise as a natural supplement to support energy and endurance in physical activities.
Quercetin Supplements:
Quercetin supplements come in various forms, both as standalone products and in combination with other ingredients. Among these, quercetin dihydrate stands out for its superior bioavailability compared to other quercetin supplements. The amount to which a substance is absorbed and used by the body is referred to as its bioavailability. Quercetin dihydrate has shown excellent absorption rates, ensuring that a higher proportion of the supplement is effectively absorbed into the bloodstream. This enhanced bioavailability allows for greater potential benefits, such as antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects, cardiovascular support, immune system modulation, and allergy relief.
Recommended Dose of Quercetin Dihydrate:
The recommended dose of quercetin dihydrate can vary depending on individual factors and the specific product. As a general guideline, a typical daily dosage range is between 500-1000 milligrams. It is advisable to start with a lower dose and gradually increase it if necessary while monitoring for any potential side effects. It is always best to follow the dosage instructions provided by the specific quercetin dihydrate supplement you are using, as formulations and concentrations may differ. If you have any underlying health conditions or are taking medications, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate dosage for your specific needs.
Side Effects and Drug Interactions:
Quercetin is generally considered safe when consumed in normal food amounts. However, in supplement form or when consumed in high doses, some individuals may experience mild side effects. These can include digestive issues like an upset stomach, nausea, diarrhea, or indigestion. It is important to note that these side effects are typically rare and not severe.
Regarding drug interactions, quercetin may interact with certain medications, potentially affecting their efficacy or increasing the risk of side effects. Quercetin has been known to interact with blood thinners, such as warfarin, and may enhance their effects, increasing the risk of bleeding. Additionally, it may interfere with certain antibiotics, such as ciprofloxacin and norfloxacin, reducing their effectiveness.
Final Thoughts:
In conclusion, quercetin dihydrate stands out as a promising supplement for promoting overall health and well-being. With its superior bioavailability and wide range of potential benefits, it is an excellent choice for individuals seeking the advantages of quercetin.
If you are interested in harnessing the power of quercetin dihydrate, we invite you to explore our brand of high-quality quercetin supplements. Our carefully formulated products prioritise purity, potency, and efficacy, ensuring that you receive the maximum benefits. Don't miss out on the opportunity to enhance your health with quercetin dihydrate. Visit our website today to learn more and make your purchase. Invest in your well-being and experience the potential of quercetin dihydrate firsthand.
Medical Disclaimer: While we have delve into the research available on the health benefits of these awesome supplements we offer, this is for informative purposes only and shouldn’t be taken as medical advice. Those who have any health-related queries should reach out to a medical professional. These statements have not been evaluated by the Therapeutic Goods Administration. This article is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.
Dr. Ayesha Tufail's LinkedIn - www.linkedin.com/in/dr-ayesha-tufail-679176252/
References:
- Jan, A. T., Kamli, M. R., Murtaza, I., Singh, J. B., Ali, A., & Haq, Q. M. R. (2010). Dietary Flavonoid Quercetin and Associated Health Benefits—An Overview. Food Reviews International, 26(3), 302–317. doi:10.1080/87559129.2010.484285
- Rauf, A., Imran, M., Khan, I. A., ur-Rehman, M.-, Gilani, S. A., Mehmood, Z., & Mubarak, M. S. (2018). Anticancer potential of quercetin: A comprehensive review. Phytotherapy Research. doi:10.1002/ptr.6155
-
Deepika, Maurya PK. Health Benefits of Quercetin in Age-Related Diseases. Molecules. 2022; 27(8):2498. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27082498
-
Kandemir, K., Tomas, M., McClements, D. J., & Capanoglu, E. (2022). Recent advances on the improvement of quercetin bioavailability. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 119, 192-200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2021.11.032
- Weng Z, Zhang B, Asadi S, Sismanopoulos N, Butcher A, Fu X, Katsarou-Katsari A, Antoniou C, Theoharides TC. Quercetin is more effective than cromolyn in blocking human mast cell cytokine release and inhibits contact dermatitis and photosensitivity in humans. PLoS One. 2012;7(3):e33805. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0033805. Epub 2012 Mar 28. PMID: 22470478; PMCID: PMC3314669.
- Lu Y, Liu Q, Yu Q. Quercetin enrich diet during the early-middle not middle-late stage of alzheimer's disease ameliorates cognitive dysfunction. Am J Transl Res. 2018 Apr 15;10(4):1237-1246. PMID: 29736217; PMCID: PMC5934583.
- Zhu M, Zhou X, Zhao J. Quercetin prevents alcohol-induced liver injury through targeting of PI3K/Akt/nuclear factor-κB and STAT3 signaling pathway. Exp Ther Med. 2017 Dec;14(6):6169-6175. doi: 10.3892/etm.2017.5329. Epub 2017 Oct 18. PMID: 29285175; PMCID: PMC5740530.
- Davis, J. Mark; Murphy, E. Angela; Carmichael, Martin D.. Effects of the Dietary Flavonoid Quercetin Upon Performance and Health. Current Sports Medicine Reports 8(4):p 206-213, July 2009. | DOI: 10.1249/JSR.0b013e3181ae8959